Understanding Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide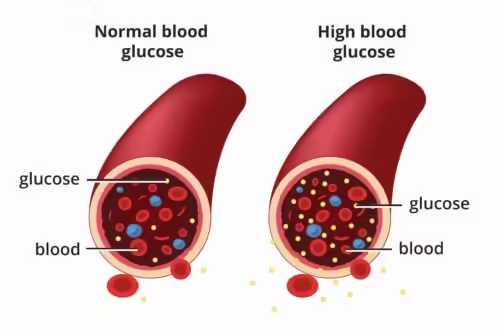
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood, which can lead to a variety of health complications if not managed properly. In this article, we will explore what diabetes is, the different types of diabetes, symptoms, causes, risk factors, and most importantly, how to manage and prevent this condition. Whether you are newly diagnosed, caring for someone with diabetes, or simply seeking to learn more, this guide provides valuable information to help you understand and navigate the world of diabetes.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that occurs when your body cannot properly process food for use as energy. Most of the food we eat is broken down into glucose, which is then used by our cells for energy. However, for glucose to enter our cells, insulin—a hormone produced by the pancreas—is required. In people with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or cannot use the insulin effectively, leading to high levels of glucose in the blood.
Understanding Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes.
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type of diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, but it can occur at any age. People with Type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy for life, as their bodies are unable to produce insulin.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for about 90-95% of all diabetes cases. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and poor diet. It can be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin therapy.
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually disappears after giving birth. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life. Managing gestational diabetes is crucial to prevent complications during pregnancy and delivery.
Symptoms of Diabetes
The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. However, common symptoms include:
- Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination: Excess glucose in the blood leads to increased urine production, which can result in dehydration and increased thirst.
- Extreme Fatigue: When cells are deprived of glucose, the body feels fatigued and lacks energy.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite eating more than usual, people with diabetes may lose weight as their bodies are unable to use glucose for energy.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can cause the lenses of the eyes to swell, leading to blurred vision.
- Slow-Healing Wounds: High blood sugar can impair circulation and reduce the body’s ability to heal wounds.
- Frequent Infections: Diabetes can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of diabetes varies depending on the type.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is primarily caused by an autoimmune reaction where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this immune reaction is still unknown, but genetic factors and environmental triggers such as viruses are believed to play a role.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Being overweight, having a sedentary lifestyle, and eating an unhealthy diet are significant risk factors. Additionally, family history and age can increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Causes of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs when the hormones produced during pregnancy interfere with the body’s ability to use insulin effectively. This condition typically develops in the later stages of pregnancy and affects women who may have risk factors such as obesity, a family history of diabetes, or being over the age of 25.
Complications of Diabetes
If left untreated or poorly managed, diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Diabetes significantly increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure.
- Neuropathy: High blood sugar can damage nerves, leading to tingling, numbness, and pain in the extremities (especially the legs and feet).
- Kidney Damage: Diabetes can cause damage to the kidneys, leading to kidney disease or even kidney failure.
- Eye Damage: Diabetes increases the risk of eye conditions such as glaucoma, cataracts, and diabetic retinopathy, which can lead to blindness.
- Foot Damage: Nerve damage in the feet can lead to ulcers, infections, and in severe cases, amputation.
- Skin Conditions: Diabetes can make the skin more susceptible to infections and other skin problems.
- Hearing Impairment: Diabetes is linked to an increased risk of hearing loss.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Type 2 diabetes may increase the risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Managing Diabetes
Effective management of diabetes is crucial to prevent complications and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle. Here are some essential strategies for managing diabetes:
1. Healthy Eating
A balanced diet is key to managing diabetes. Focus on:
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to get a wide range of nutrients.
- Lean Proteins: Include lean proteins such as chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes.
- Healthy Fats: Opt for healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds.
- Portion Control: Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid overeating and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
2. Regular Physical Activity
Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Additionally, include strength training exercises at least twice a week to build muscle and support overall health.
3. Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes. This helps you understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your blood sugar and allows you to make necessary adjustments to stay within your target range.
4. Medication and Insulin Therapy
Depending on the type and severity of diabetes, your doctor may prescribe oral medications or insulin therapy to help manage blood sugar levels. It’s crucial to take medications as prescribed and discuss any side effects or concerns with your healthcare provider.
5. Stress Management
Stress can impact blood sugar levels, so finding effective ways to manage stress is important. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and regular physical activity can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
6. Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular visits to your healthcare provider are important for monitoring your condition and preventing complications. Your doctor will check your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, kidney function, and eye health to ensure that your diabetes is well-managed.
Prevention of Diabetes
While Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, Type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes can often be prevented or delayed through lifestyle changes. Here are some tips for reducing your risk of developing diabetes:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight is a significant risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Losing even a small amount of weight (5-10% of your body weight) can reduce your risk.
2. Be Physically Active
Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, improves insulin sensitivity, and lowers blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
3. Eat a Balanced Diet
Focus on a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
4. Avoid Smoking
Smoking increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and its complications. If you smoke, seek help to quit.
5. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation.
6. Get Regular Screenings
If you have risk factors for diabetes, such as being overweight, having a family history of diabetes, or being over 45, regular screenings can help detect diabetes early and allow for prompt management.
Living with Diabetes
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but with the right tools and support, it is possible to lead a healthy and fulfilling life. Here are some tips for managing diabetes on a daily basis:
1. Educate Yourself
The more you know about diabetes, the better equipped you will be to manage it. Attend diabetes education classes, read reliable sources, and stay informed about new developments in diabetes care.
2. Build a Support System
Having a strong support system can make managing diabetes easier. Connect with family, friends, and support groups who understand what you are going through.
3. Set Realistic Goals
Set achievable goals for managing your diabetes, such as improving your diet, increasing physical activity, or losing weight. Celebrate your successes and learn from any setbacks.
4. Take Care of Your Mental Health
Living with a chronic condition like diabetes can take a toll on your mental health. Don’t hesitate to seek help from a mental health professional if you feel overwhelmed, anxious, or depressed.
5. Stay Positive
Managing diabetes is a lifelong commitment, but with the right approach, you can live a long and healthy life. Focus on the positive aspects of your health and well-being, and remember that you have the power to make choices that will improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex and challenging condition, but with proper management, it is possible to live a healthy and active life. By understanding the different types of diabetes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can take control of your condition and reduce the risk of complications. Whether you are living with diabetes or supporting someone who is, education, support, and self-care are key to successfully managing this condition.
By following the tips and strategies outlined in this article, you can effectively manage your diabetes and lead a fulfilling life. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.



